Introduction
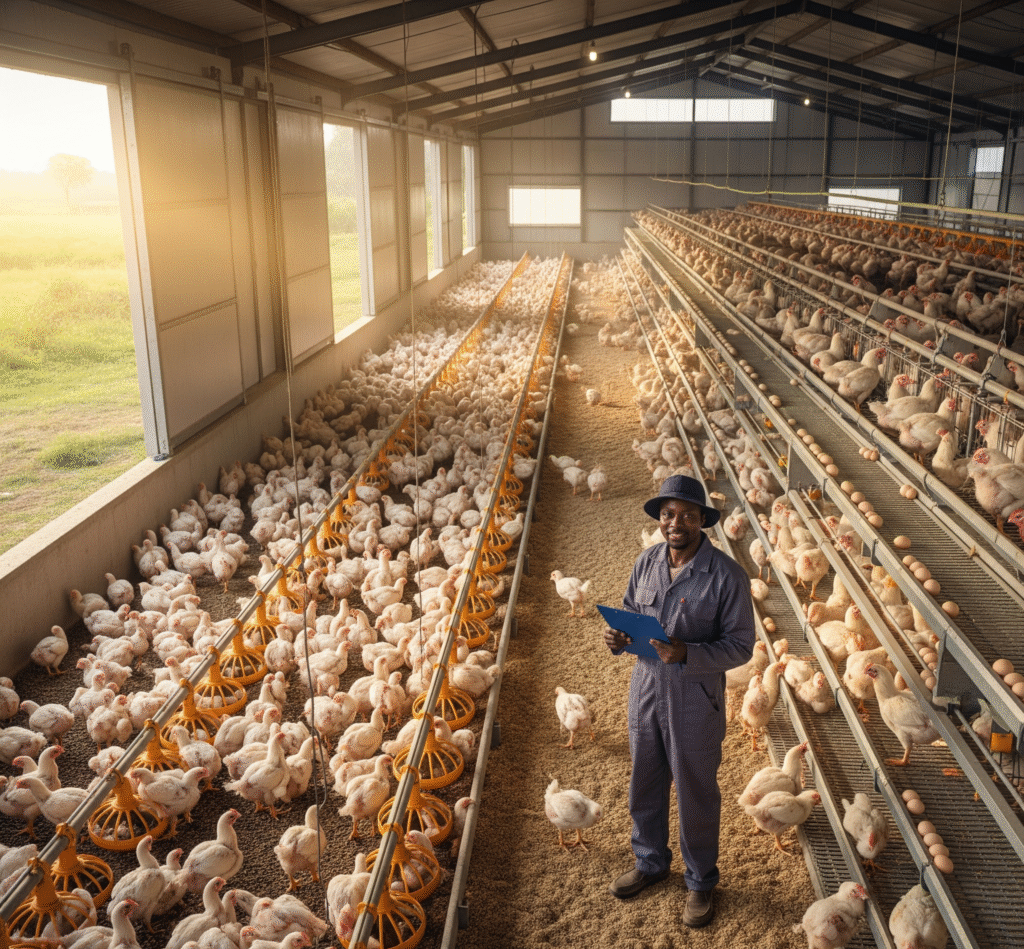
Poultry farming is one of the fastest growing agribusiness sectors in Africa and around the world. With rising demand for eggs and chicken meat, it offers both quick returns and long term profitability when managed correctly.
This guide provides a comprehensive, step by step plan for beginners to set up and run a profitable poultry farm within 90 days, focusing on best practices for both broiler and layer production.
1. Understanding Poultry Farming
Poultry farming involves the raising of domesticated birds primarily chickens for meat (broilers) or eggs (layers).
Why it’s a profitable choice:
High demand: Poultry products are consumed daily across households, hotels, restaurants, and institutions.
Quick turnaround: Broilers can be ready for market in 6–8 weeks.
Scalability: Start small and expand as capacity and resources grow.
Diverse income streams: Meat sales, egg sales, manure for organic fertilizer.
2. Choosing Your Production Type
Before starting, decide which category best suits your goals, budget, and timeline.
Broilers

- Raised for meat.
- Harvest period: 6–8 weeks.
- Quick return on investment.
- Requires immediate market readiness before harvest.
Layers

Raised for egg production.
Laying starts: 18–22 weeks of age.
Continuous daily income for 12–18 months.
Requires more patience but provides consistent cash flow.
3. Setting Up Your Farm
Proper setup is critical to bird health, productivity, and profitability.
Location
- Away from residential areas (to minimize noise, odour, and disease risk).
- Good road access for feed supply and product delivery.
- Reliable source of clean water.
- Security against theft and predators.
Housing
- Well-ventilated, dry, and easy to clean.
- Adequate lighting for growth and egg production.
- Deep litter system (wood shavings, rice husk) or battery cage system for layers.
- Protection from extreme heat, cold, and rain.
Space requirements:
Broilers: 1 sq. ft per bird.
Layers: 1.5–2 sq. ft per bird.
4. Sourcing Day-Old Chicks (DOCs)
The quality of your chicks determines the potential success of your farm.
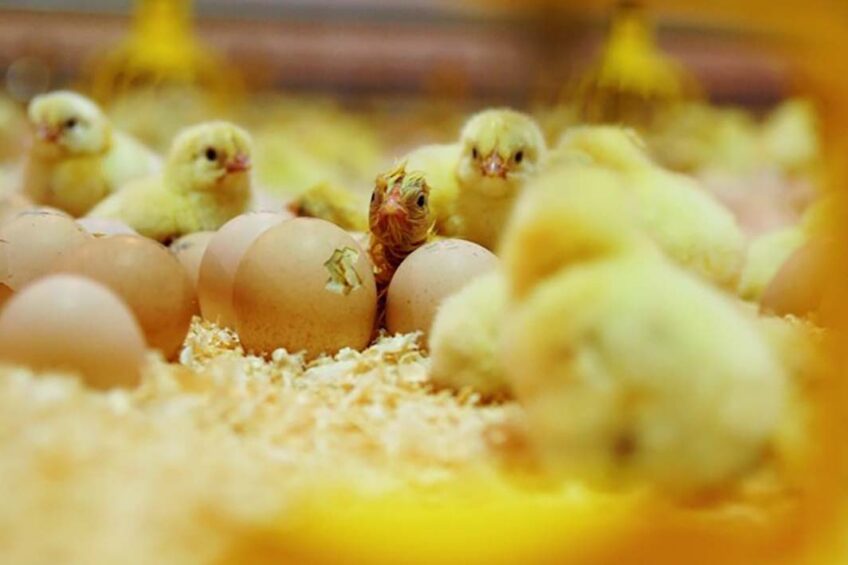

Buy from reputable hatcheries with proven vaccination programs.
Inspect chicks for alertness, bright eyes, clean vents, and good feathering.
Transport early in the morning to reduce heat stress.
5. Feeding and Nutrition
Feed is the largest cost in poultry farming (about 70% of expenses) and directly affects growth, egg production, and profits.
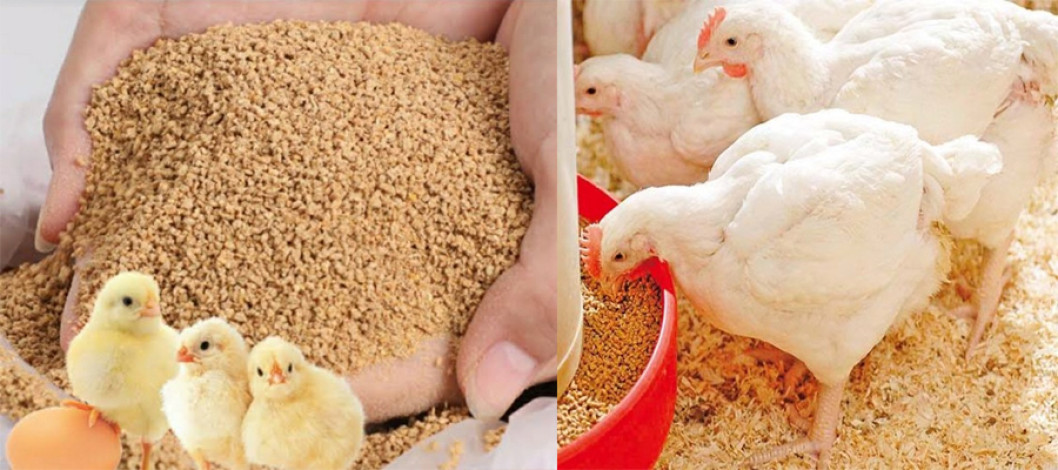

Broiler Feeding Schedule:
Starter feed: 0–4 weeks.
Grower feed: 4–6 weeks.
Finisher feed: 6 weeks to market.
Layer Feeding Schedule:
Chick starter: 0–6 weeks.
Grower mash: 6–18 weeks.
Layer mash: from 18 weeks onwards.
Key tips:
Provide clean, fresh water at all times.
Store feed in a cool, dry place to avoid spoilage.
Do not switch feed brands unnecessarily.
6. Health Management
Maintaining flock health ensures productivity and reduces losses.
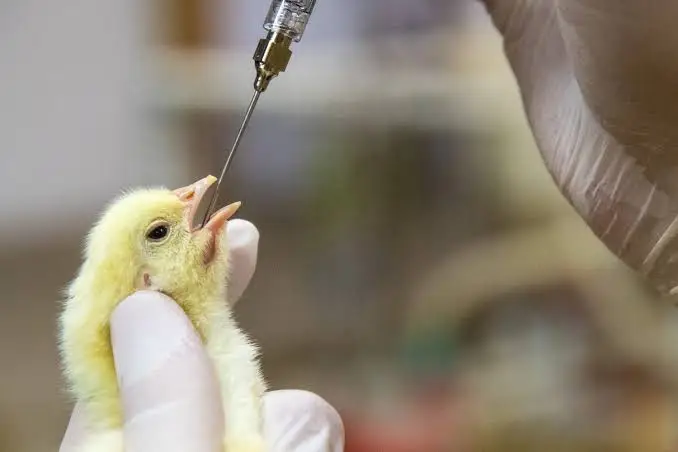
Vaccination Program:
Follow a standard vaccination schedule for Newcastle disease, Gumboro, Fowl Pox, and other common poultry diseases.
Biosecurity Measures:
Limit farm access to essential personnel.
Use foot dips and hand sanitizers.
Regular cleaning and disinfection of equipment.
Isolate and treat sick birds immediately.
7. Record Keeping
Accurate records allow you to monitor performance, control costs, and make informed decisions.
Track:
Feed consumption.
Mortality rates.
Medication and vaccination schedules.
Egg production (for layers).
Sales and expenses.
Digital tools like Agrofiat Smartfarm can automate this process, providing real-time insights for better decision-making.
8. Marketing
Develop a sales strategy before you start production.
For Broilers:
Target restaurants, hotels, caterers, coldrooms, and live bird markets.
Sell in bulk to reduce transportation costs and time.
For Layers:
Build relationships with egg vendors, bakeries, supermarkets, and institutions.
Consider direct to consumer sales for higher margins
9. The 90-Day Broiler Farming Timeline
Before starting, decide which category best suits your goals, budget, and timeline.
Day 1–7

Receive chicks, set up brooder, maintain temperature at 32–35°C.
Provide starter feed and clean water.
First vaccinations.
Day 8–28:
Monitor growth.
Continue vaccination program.
Adjust feed quantities as birds grow.

Day 29–42:

Final vaccinations if needed.
Reduce stocking density if required.
Confirm sales agreements.
Day 43–56:
Harvest and sell birds.
Clean and disinfect housing before the next cycle.

10. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Overcrowding birds.
Buying cheap, low-quality chicks.
Skipping vaccinations.
Poor feed storage leading to contamination.
Delaying sales beyond peak market weight.
Conclusion
Poultry farming is a high potential agribusiness when approached with the right knowledge, discipline, and systems in place. By focusing on proper housing, quality feeding, strict health management, and reliable record keeping, you can achieve profitability within 90 days and scale steadily over time.
Using digital management tools like Agrofiat Smartfarm ensures transparency, efficiency, and investor confidence critical factors for sustainable growth in modern agriculture.

